UIScrollView 拖动时执行的是 UITrackingRunLoopMode,会导致暂停定时器,等恢复为 NSDefaultRunLoopMode 时才恢复定时器。
所以如果需要定时器在 UIScrollView 拖动时也不影响的话,建议添加到 UITrackingRunLoopMode 或 NSRunLoopCommonModes 中:
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:5 target:self selector:@selector(timerAction) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode: UITrackingRunLoopMode]; ///< 或者 NSRunLoopCommonModes
1. NSTimer
//创建方式1
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(action:) userInfo:nil repeats:NO];
[timer invalidate];
//调用创建方法后,target对象的计数器会加1,直到执行完毕,自动减1。如果是循环执行的话,就必须手动关闭,否则可以不执行释放方法。
TimerInterval : 执行之前等待的时间。比如设置成1.0,就代表1秒后执行方法
target : 需要执行方法的对象。
selector : 需要执行的方法
repeats : 是否需要循环
//推荐-->创建方式2
使用上面的创建方式,会自动把timer加入MainRunloop的NSDefaultRunLoopMode中。如果使用以下方式创建定时器,就必须手动加入Runloop:
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:5 target:self selector:@selector(timerAction) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
[timer invalidate];
存在延迟:不管是一次性的还是周期性的timer的实际触发事件的时间,都会与所加入的RunLoop和RunLoop Mode有关,如果此RunLoop正在执行一个连续性的运算,timer就会被延时出发。
2. CADisplayLink
- (void)startDisplayLink{
self.displayLink = [CADisplayLink displayLinkWithTarget:self
selector:@selector(handleDisplayLink:)];
[self.displayLink addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]
forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
}
- (void)handleDisplayLink:(CADisplayLink *)displayLink{
//do something
}
- (void)stopDisplayLink{
[self.displayLink invalidate];
self.displayLink = nil;
}
CADisplayLink是一个能让我们以和屏幕刷新率同步的频率将特定的内容画到屏幕上的定时器类。 CADisplayLink以特定模式注册到runloop后, 每当屏幕显示内容刷新结束的时候,runloop就会向 CADisplayLink指定的target发送一次指定的selector消息, CADisplayLink类对应的selector就会被调用一次。所以通常情况下,按照iOS设备屏幕的刷新率60次/秒
iOS设备的屏幕刷新频率是固定的,CADisplayLink在正常情况下会在每次刷新结束都被调用,精确度相当高。使用场合相对专一,适合做UI的不停重绘,比如自定义动画引擎或者视频播放的渲染。不需要在格外关心屏幕的刷新频率了,本身就是跟屏幕刷新同步的。
#####延迟
iOS设备的屏幕刷新频率是固定的,CADisplayLink在正常情况下会在每次刷新结束都被调用,精确度相当高。但如果调用的方法比较耗时,超过了屏幕刷新周期,就会导致跳过若干次回调调用机会。
如果CPU过于繁忙,无法保证屏幕60次/秒的刷新率,就会导致跳过若干次调用回调方法的机会,跳过次数取决CPU的忙碌程度。
#####使用场景
从原理上可以看出,CADisplayLink适合做界面的不停重绘,比如视频播放的时候需要不停地获取下一帧用于界面渲染。
对于iOS设备来说刷新频率就是60HZ,也就是说selector的调用是每秒60次。
但是CADisplayLink的调用真的足够精确吗?因为我们知道,fps这个东西可不是一成不变的!
some++;
if (some==60) {
some=0;
NSLog(@"一秒 !!");
}
也就意味着,如果每秒调用60次的话,那么输出应该是每秒一次。
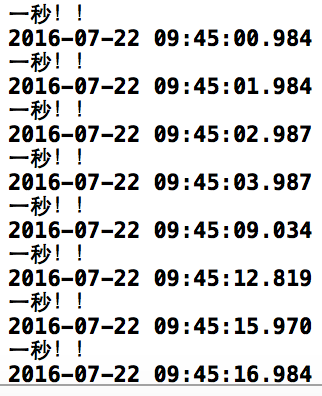
可以看到输出中的时间。一开始是很平稳的45:01,45:02,45:03,然后一下子跳到了45:09,然后又是45:12,45:15,可以看到,并不是确定的每秒输出一次,也就是并不是每秒调用60次selector!
那么为什么一开始那么平稳,突然就变了呢。我在一个tableView中,每个cell加了很多复杂的UI,所以GPU去渲染时很耗费性能,导致fps并不能以60的平稳状态保持,selector的调用也就相应的变化了。
结论
CADisplayLink的调用足够精确吗?
答:CADisplayLink每当屏幕刷新一次就会调用一次selector,非常精确。但是,应为屏幕刷新并不是一成不变的每秒60次,所以每秒调用固定次数的说法并不正确!
(虽然一个好的应用,fps应该相对平稳)
3. GCD
1. 执行一次
double delayInSeconds = 2.0;
dispatch_time_t popTime = dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, delayInSeconds * NSEC_PER_SEC);
dispatch_after(popTime, dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^(void){
//执行事件
});
2. 重复执行
NSTimeInterval period = 1.0; //设置时间间隔
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_source_t _timer = dispatch_source_create(DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE_TIMER, 0, 0, queue); <br> dispatch_source_set_timer(_timer, dispatch_walltime(NULL, 0), period * NSEC_PER_SEC, 0); //每秒执行
dispatch_source_set_event_handler(_timer, ^{
//在这里执行事件
});
dispatch_resume(_timer);
GCD的定时器和NSTimer是不一样的,NSTimer受RunLoop影响,但是GCD的定时器不受影响,因为RunLoop也是基于GCD的
计时器(全局)
@interface ViewController ()
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSTimer *timer; // timer
@property(nonatomic,assign)int countDown; // 倒数计时用
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSDate *beforeDate; // 上次进入后台时间
@end
static int const tick = 60;
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self setupNotification];
[self startCountDown];
}
-(void)dealloc {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]removeObserver:self name:UIApplicationDidEnterBackgroundNotification object:nil];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]removeObserver:self name:UIApplicationWillEnterForegroundNotification object:nil];
[self stopTimer];
}
-(void)setupNotification {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]addObserver:self selector:@selector(enterBG) name:UIApplicationDidEnterBackgroundNotification object:nil];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]addObserver:self selector:@selector(enterFG) name:UIApplicationWillEnterForegroundNotification object:nil];
}
/**
* 进入后台记录当前时间
*/
-(void)enterBG {
NSLog(@"应用进入后台啦");
_beforeDate = [NSDate date];
}
/**
* 返回前台时更新倒计时值
*/
-(void)enterFG {
NSLog(@"应用将要进入到前台");
NSDate * now = [NSDate date];
int interval = (int)ceil([now timeIntervalSinceDate:_beforeDate]);
int val = _countDown - interval;
if(val > 1){
_countDown -= interval;
}else{
_countDown = 1;
}
}
/**
* 开始倒计时
*/
-(void)startCountDown {
_countDown = tick; //< 重置计时
_timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(timerFired:) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; //< 需要加入手动RunLoop,需要注意的是在NSTimer工作期间self是被强引用的
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:_timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes]; //< 使用NSRunLoopCommonModes才能保证RunLoop切换模式时,NSTimer能正常工作。
}
-(void)timerFired:(NSTimer *)timer {
if (_countDown == 0) {
[self stopTimer];
NSLog(@"重新发送");
}else{
_countDown -=1;
NSLog(@"倒计时中:%d",_countDown);
}
}
- (void)stopTimer {
if (_timer) {
[_timer invalidate];
}
}
雪花效果
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIImage *imgSnowflake;
@end
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
- (void)layoutUI;
- (void)snow;
@end
@implementation ViewController
#define kApplicationFrame [[UIScreen mainScreen] applicationFrame]
#define kWidthOfSnowflake 30.0
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self layoutUI];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
- (void)layoutUI {
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.218 green:0.219 blue:0.196 alpha:1.000];
_imgSnowflake = [UIImage imageNamed:@"Snowflake"];
//定时器;每隔0.5秒执行一次
[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:0.5
target:self
selector:@selector(snow)
userInfo:nil
repeats:YES];
}
- (void)snow {
NSString *strWidthOfScene = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%f", kApplicationFrame.size.width-kWidthOfSnowflake]; //bounds 返回整个屏幕大小;applicationFrame 返回去除状态栏后的屏幕大小
CGFloat startX = arc4random()%[strWidthOfScene integerValue]; //产生随机数0到strWidthOfScene-1
CGFloat endX = (arc4random()%[strWidthOfScene integerValue]) + 1; //产生随机数1到strWidthOfScene
UIImageView *imgV = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:_imgSnowflake];
imgV.frame = CGRectMake(startX, -20.0, kWidthOfSnowflake, kWidthOfSnowflake);
imgV.alpha = 0.8;
[self.view addSubview:imgV];
[UIView beginAnimations:nil context:NULL];
[UIView setAnimationDuration:5];
imgV.frame = CGRectMake(endX,
kApplicationFrame.size.height+20.0-kWidthOfSnowflake,
kWidthOfSnowflake,
kWidthOfSnowflake);
[UIView commitAnimations];
}
@end

